Glossary and Concepts
Since the inception of “High Throughput Computing” in 1996 the PATh partners have coined many terms and concepts to help better describe their computational methodology. Below are the terms that have been introduced and a description of each.
High Throughput Computing (HTC)
Maximizing the throughput of a computing resource toward a common problem.
Distributed High Throughput Computing (dHTC)
Specialized by the OSG, dHTC involves running a HTC infrastructure across many independent, collaborating administrative domains.
OSG Consortium
A consortium dedicated to the advancement of all of Open Science via the practice of distributed High Throughput Computing, and the advancement of its state of the art.
The OSG Consortium provides a fabric of services, including a software stack, that organizations can use to build dHTC environments. These services can be used by resource providers to build dHTC environments.
- The consortium coordinates the efforts contributed by projects such as the NSF-funded IRIS-HEP and PATh.
- One important service in the OSG fabric of services is the Open Science Pool.
HTCondor Software Suite (HTCSS)
HTCSS, based out of the Center for High Throughput Computing at UW-Madison, implements several technologies for creating a dHTC environment.
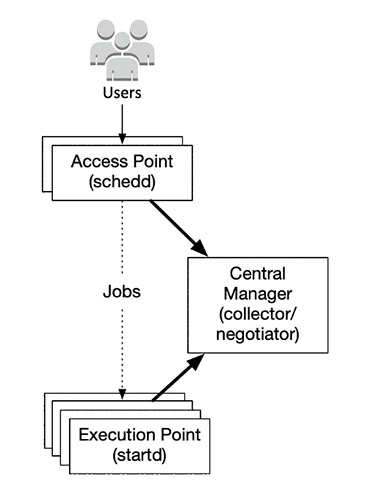
Access Point (AP)
Users can place their workloads (such as jobs, job sets, and DAGs) at an Access Point. The Access Point accesses one or more resource pools to acquire resources.
Execution Point (EP)
The Execution Point is given jobs by an Access Point and executes them.
Central Manager (CM)
Locates daemons and allocates shares of the overall resource pool.
Compute Entrypoint (CE)
Provides a mechanism to integrate a local resource (such as a batch system) with the outside world.
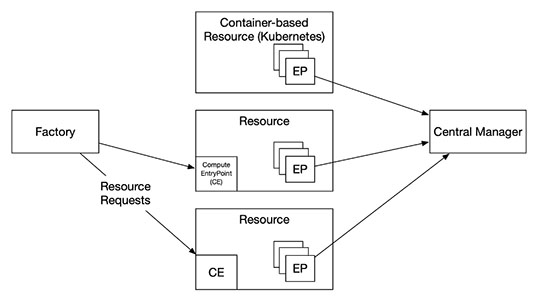
Open Science Compute Federation (OSCF)
The OSCF provides a set of services for requesting and allocating computing resources and creating dHTC environments.
- The Compute Entrypoint, hosted on-premises or off-premises, provides a way for the factory to send resource requests to a compute resource.
- The factory acts on behalf of an organization that requests resources.
- If HTCSS is used by the organization, each resource starts an Execution Point and joins a Central Manager.
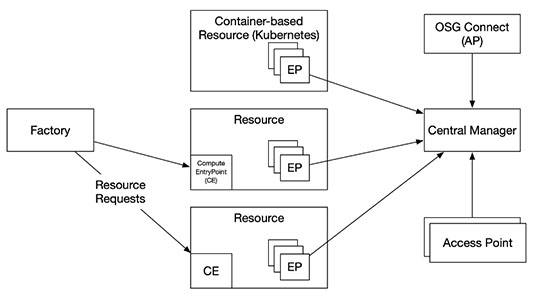
Open Science Pool (OSPool)
An environment for any scientist or group doing open science in the US.
- Any campus, group, or collaboration can attach an access point to the OSPool and receive a share of the resources.
- OSG-Operated Access Points are meant to provide a place for PI-driven groups to place their jobs.
- Users can Bring Your Own Resources (BYOR) to utilize their own resources (such as an XRAC allocation) via the OSPool.
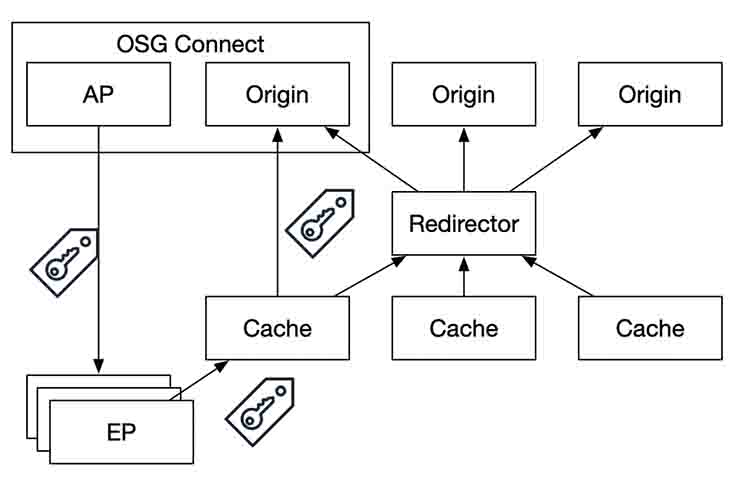
Open Science Data Federation (OSDF)
The OSDF is a set of federated origin and cache services that coordinate a namespace for data access.
- Jobs at an Execution Point can access data via the OSDF, potentially authorized by an access token.
- The OSDF system serves the data from the closest cache, retrieving it from an origin via the OSDF redirector if not on the local disk of the cache.
- OSG-Operated Access Points provides an origin service which users can place data in or users can attach their own storage to serve as an origin.